


Chiral carbon in glucose full#
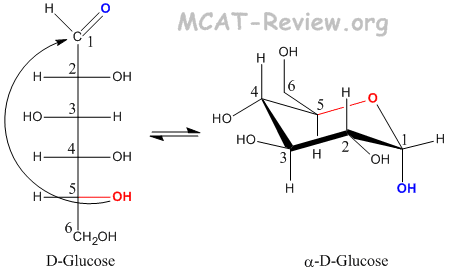
What I wanted to do in this video is familiarize ourselves with one of the most important molecules in biology And that is Glucose sometimes referred to as Dextrose and the term Dextrose comes from the fact that the form of Glucose typically Typically found in nature if you form a solution of it, it's going to polarize light to the right and Dextre means Right But the more typical term glucose this literally means sweet in greek if you ask a greek friend to say sweet it sounds like Lucas or I'm not saying it perfectly, but it sounds a lot like a glucose And that's because that's where the word comes from and it is super important because it is it is it is how energy stored and transferred in biological systems in fact right when if someone were to talk about your blood your blood sugar they're talking about the glucose content, so when people talk about blood blood sugar they're talking about your they're talking about your glucose content the whole process of photosynthesis this is all about plants using harnessing the energy and storing that energy in the form of glucose when we talk about when we talk about things like respiration in our in our cells cellular respiration that's all about taking glucose and using it to full and to create atp's which are the molecular currency of energy Inside of our body, so these are in credit is an incredibly important molecule We can start wreaking chains of glucose to form Glycogen to form Starches this along with another similar another simple sugar fructose you can use to form our table sugar But even glucose by itself is sweet so let's get familiar with it as a molecule so immediately When you look at this is it kind of drawn as a as an open chain we see that we have one two three Actually, let me number these we have one two three four five six carbons, so chemical formula would be C sub six a subscript of six we have how many hydrogen's How many hydrogen's we have we have 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 hydrogen's? C6H12 and then we have how many oxygens do we have? Have one two three four five six oxygens Six oxygens, so you might notice we have six carbons and then the ratio for every one oxygen We have two hydrogen's which is really the ratio of Hydrogen's to oxygens in Water and if we want to really if we really want to if we add obviously here We don't have just two hydrogen's and one oxygen We have 12 hydrogen's and six oxygens, but it's really good to even just familiarize yourselves with what are the different parts here So we see on the number one carbon it is part of a carbonyl group when a carbon is bonded to double bonded to an oxygen like that.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
